Docker for Developer
⚠️
This project is not a course or a guide, I just take personal notes for a quick reference.
Using database with docker
In this notes I’ll create a docker-compose.yml file or a specific name YAML file to set up and run a MySQL or PostgreSQL.
⚠️ In both examples, we are changing the default ports to avoid conflicts if another instance of the same database or container is already running on the default ports. By specifying different ports, we ensure that our Docker containers can coexist peacefully without encountering port conflicts. This practice is especially useful in development environments where multiple services may be running simultaneously.
PostgreSQL Setup with Docker
This section can include all the instructions and configurations related to setting up PostgreSQL using Docker.
version: '3.8'
services:
postgres_dockertest:
container_name: postgres_dockertest
image: postgres
ports:
- 5431:5432 # Changing the default port 5432 to port 5431.
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=admin
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=admin
- POSTGRES_DB=dockertestTwo ways to start this YAML file
docker-compose up -dif the file has default namedocker-compose.ymldocker-compose -f docker-compose-PostgreSQL.yml up -dif the file has a specific name likedocker-compose-PostgreSQL.yml
PS C:\GitHub\dockertest> docker-compose -f docker-compose-PostgreSQL.yml up -d
[+] Running 1/2
- Network dockertest_default Created 0.9s
✔ Container postgres_dockertest Started 0.8s
PS C:\GitHub\dockertest>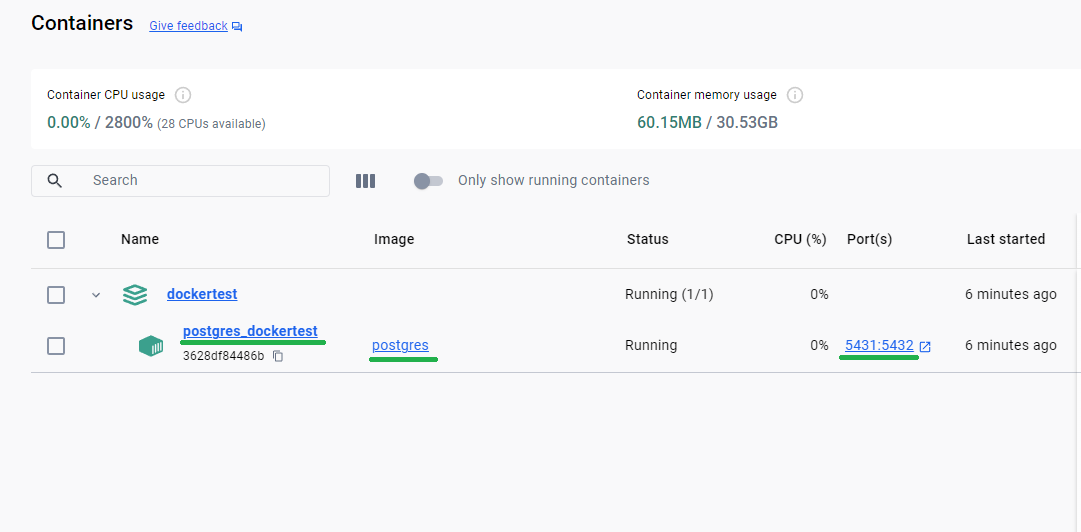
server.port=8085
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5431/dockertest
spring.datasource.username=admin
spring.datasource.password=admin
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=trueMySQL Setup with Docker
Similarly, this section can encompass all the details and steps required for setting up MySQL using Docker.
version: '3.8'
services:
mysql_dockertest:
container_name: mysql_dockertest
image: mysql:8.0
ports:
- 3305:3306 # Changing the default port 3306 to port 3305.
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin
- MYSQL_DATABASE=dockertest
volumes:
- mysql_data:/var/lib/mysql
volumes:
mysql_data:Two ways to start this YAML file
docker-compose up -dif the file has default namedocker-compose.ymldocker-compose -f docker-compose-MySQL.yml up -dif the file has a specific name likedocker-compose-MySQL.yml
PS C:\GitHub\dockertest> docker-compose -f docker-compose-MySQL.yml up -d
[+] Running 1/1
✔ Container mysql_dockertest Started 0.4s
PS C:\GitHub\dockertest>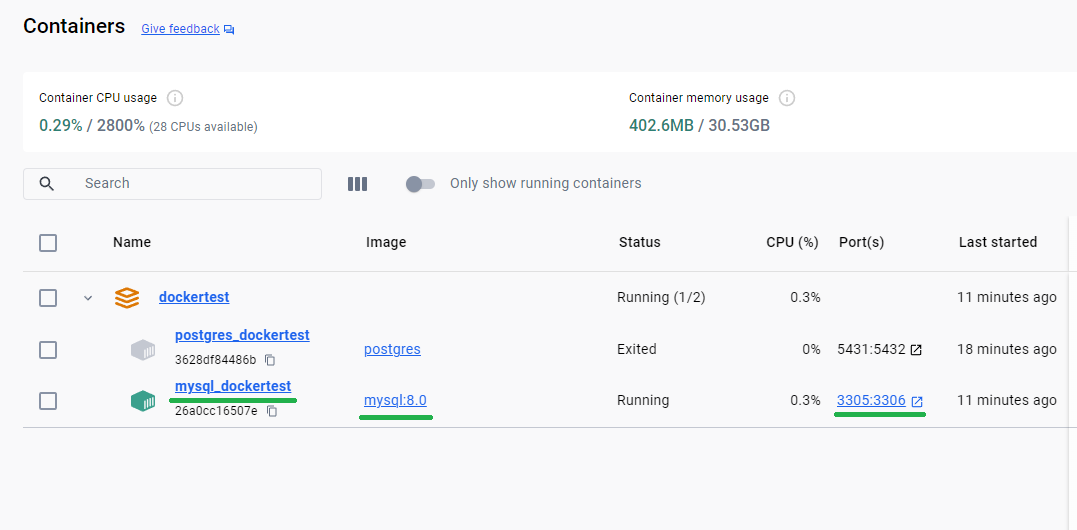
server.port=8085
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3305/dockertest
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=admin
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true⚠️ For DBeaver users
Right-click on your connection and select "Edit Connection".
In the "Connection Settings" screen, navigate to "Driver Properties".
Right-click on the "user properties" area and choose "Add new property".
Add the following two properties:
Property Name:
useSSLValue:falseProperty Name:
allowPublicKeyRetrievalValue:true
Source: Alura Forum
Test
package br.com.rasiaink.dockertest;
import br.com.rasiaink.dockertest.model.User;
import br.com.rasiaink.dockertest.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class StartApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private UserRepository repository;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setName("Tiago");
user.setUsername("rasia83");
user.setPassword("123456-don't-do-it");
repository.save(user);
for(User u: repository.findAll()){
System.out.println(u);
}
}
}package br.com.rasiaink.dockertest.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.*;
import org.hibernate.proxy.HibernateProxy;
import java.util.Objects;
@Entity
@Table(name = "tab_user")
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id_user")
private Integer id;
@Column(length = 50, nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(length = 50, nullable = false)
private String username;
@Column(length = 50, nullable = false)
private String password;
public User(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null) return false;
Class<?> oEffectiveClass = o instanceof HibernateProxy ? ((HibernateProxy) o).getHibernateLazyInitializer().getPersistentClass() : o.getClass();
Class<?> thisEffectiveClass = this instanceof HibernateProxy ? ((HibernateProxy) this).getHibernateLazyInitializer().getPersistentClass() : this.getClass();
if (thisEffectiveClass != oEffectiveClass) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return getId() != null && Objects.equals(getId(), user.getId());
}
@Override
public final int hashCode() {
return this instanceof HibernateProxy ? ((HibernateProxy) this).getHibernateLazyInitializer().getPersistentClass().hashCode() : getClass().hashCode();
}
}package br.com.rasiaink.dockertest.repository;
import br.com.rasiaink.dockertest.model.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
}Result
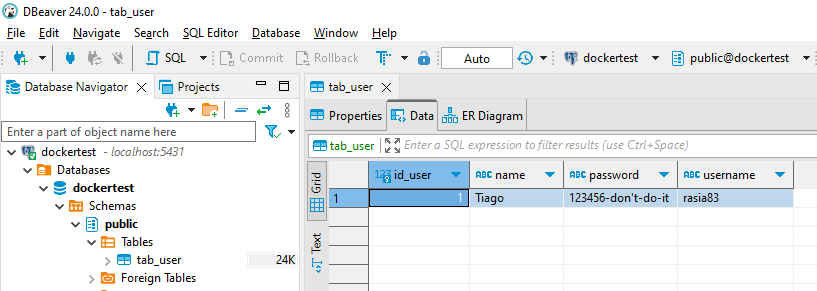
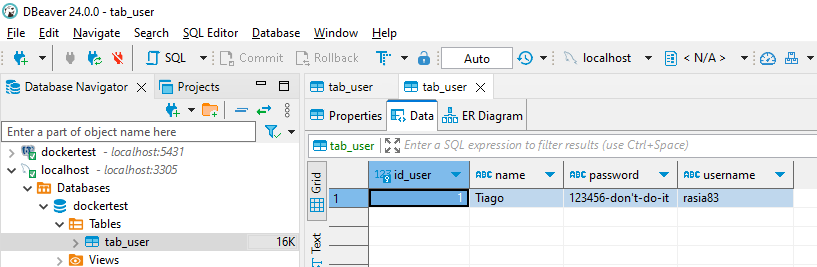
Extra 1
Add a .sql file to start with MySQL and an exemple to create a user
First create a .SQL file in the same folder as Docker YAML file.
For this sample to add a user in MySQL, I'll create a create-user.sql
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS 'developer'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'dev123';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON dockertest.* TO 'developer'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Now change my docker file to add this SQL file.
version: '3.8'
services:
mysql_dockertest:
container_name: mysql_dockertest
image: mysql:8.0
ports:
- 3305:3306 # Changing the default port 3306 to port 3305.
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=admin
- MYSQL_DATABASE=dockertest
- MYSQL_INIT_SQL=/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sql
volumes:
- mysql_data:/var/lib/mysql
- ./create-user.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sqlapplication.properties with the new user
server.port=8085
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3305/dockertest
spring.datasource.username=developer
spring.datasource.password=dev123
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=trueExtra 2
Neo4J
version: "3.8"
services:
neo4j:
image: neo4j:community
ports:
- 7474:7474
- 7687:7687
# This binds two ports (7474 and 7687) for HTTP and Bolt access to the Neo4j API.
# which allows you to access neo4j through your browser at http://localhost:7474
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- NEO4J_AUTH=neo4j/password # login / password
volumes:
- ./db/data:/data
- ./db/conf:/conf
- ./db/logs:/logs
- ./db/plugins:/plugins